本文发布于61 天前,其中的信息可能已经过时,如有错误请发送邮件到supper@vcclient.xyz
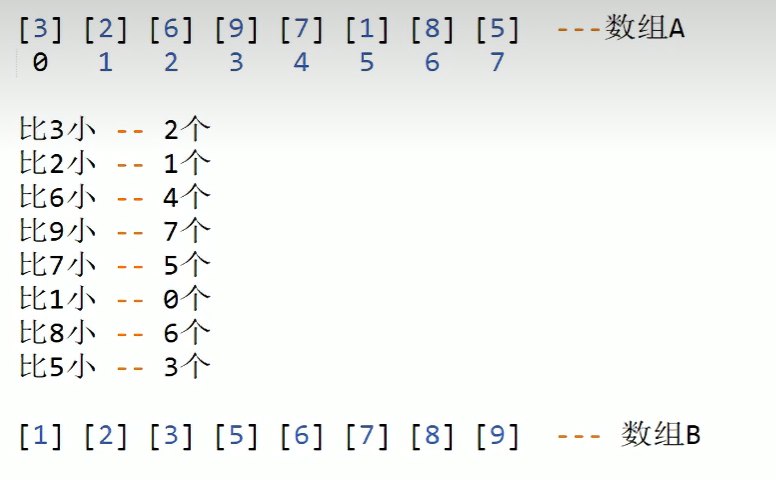
统计数组A中的比每个元素小的元素个数,并把该个数作为数组B的下标
/******************************************************************************
*
* file name : 计数排序
* author : Wzy
* data : 2025/12/15
* function : 统计数组A中的比每个元素小的元素个数,并把该个数作为数组B的下标
* note : None
*
* copyRight (c) 2025 17630246607@163.com All Right Reseverd
* ****************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
/******************************************************************************
*
* func name : CountSort
* function : 实现计数排序
* argument :
* @A[]:待统计的数组
* @size:数组中元素的个数
* @B[]:新数组
* retval : None
* author : Wzy
* date : 2025/12/15
* note : None
*
* ****************************************************************************/
void CountSort(int A[],int B[],int size)
{
int cnt = 0; //记录个数
for (int n = 0; n < size; ++n)
{
cnt = 0; //计数器清0;
//n作为数组A的元素的下标
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
if (A[i] < A[n]) //A[n]为当前元素,A[i]是数组中的所有元素
{
cnt ++;
}
}
B[cnt] = A[n];
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
//定义一个整形数组存储10个整数
int A[11] = {14,23,12,5,8,3,9,10,33,6,11};
int B[11] = {0};
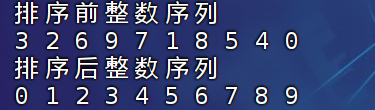
printf("排序前整数序列\n");
for (int i = 0; i <sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); ++i)
{
printf("%d ",A[i]);
}
printf("\n");
CountSort(A,B,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
printf("排序后整数序列\n");
for (int i = 0; i <sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]); ++i)
{
printf("%d ",B[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}测试结果